What is a Slot-Die Coater? A Guide to Precision Thin-Film Coating
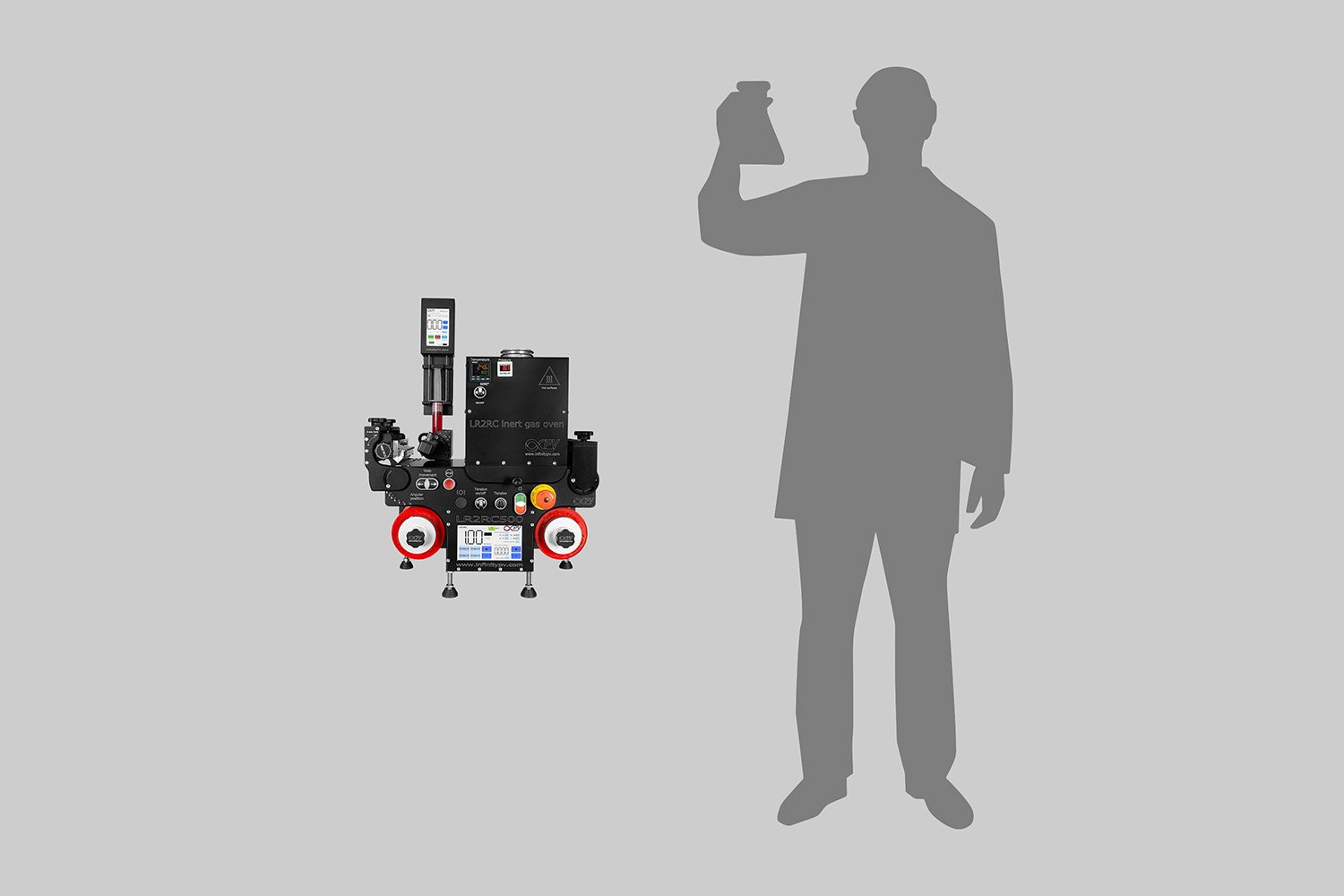
Example of a compact roll-to-roll slot-die coater.
A slot-die coater is a specialized equipment used in the application of thin and uniform films of solutions or slurries onto a substrate by applying a slot-die head. Slot-die coaters are utilized across a variety of industries and these benefit from the precision, scalability, and efficiency of slot-die coating technology, allowing to produce high-quality thin films essential for advanced applications.
What is Slot-Die Coating?
Slot-die coating is a process where a liquid material is dispensed through a narrow slot onto a substrate, creating a controlled, even film. This method is widely used because it provides unparalleled control over coating thickness and uniformity. Researchers and manufacturers rely on slot-die coating for applications that demand high precision and repeatability.
Unlike traditional coating methods like spin-coating or dip-coating, slot-die coating offers numerous advantages:
High material efficiency (minimal waste, since only the required amount of material is used)
Excellent uniformity (consistent layer thickness across the entire substrate)
Scalability (applicable from small laboratory samples to industrial-scale production)
Versatility (suitable for various materials, including functional inks, adhesives, and nano-material dispersions)
This technology enables researchers and manufacturers to produce high-quality films while minimizing material loss, making it both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
Discover everything you need to know about slot-die coating in our comprehensive guide.
What Are the Key Components of a Slot-die Coater?
A slot-die coater consists of several components that work together to ensure the precise application of thin films onto substrates and foils.
Slot-die Head: The slot-die head contains a narrow slot through which the coating material is dispensed. It is designed to create a consistent and uniform film thickness as the substrate moves underneath. The width and design of the slot opening are critical, as they determine the flow rate of the liquid coating and the film thickness. Adjustments can typically be made to accommodate different materials and desired film properties.
Pumping System: A pumping system, which may include syringe pumps, gear pumps or diaphragm pumps, is responsible for delivering the coating material from the reservoir to the die head at a controlled rate.
Substrate Transport System: This system moves the substrate (such as film, paper, or glass) under the slot-die head, or it moves the slot-die head over the substrate at a set speed. The accuracy of the substrate or slot-die head movement is essential for achieving uniform film application. The substrate transport system in a slot-die coater can be designed for both sheet-based and roll-to-roll (R2R) applications.
Drying and Curing: In the slot-die coating of thin films, drying and or curing is also a critical step that influences the final properties of the film. Drying at elevated temperatures is employed to ensure effective solvent removal and to achieve the desired film characteristics and curing with UV light can be used to activate chemical reactions, such as cross-linking or polymerization.
Control System: The control system allows the operator to regulate the key parameters of the coating process, including material flow rate, coating speed, position of the slot-die head over the substrate and power of the drying and curing units. This ensures consistent and repeatable results.
The infinityPV Slot-die Coater can be customized to suit your specific needs.
Sheet-Based vs. Roll-to-Roll (R2R) Slot-Die Coating
There are two primary ways to implement slot-die coating: sheet-based and roll-to-roll (R2R) based. Each method has distinct benefits and is suited for different applications.
Sheet-Based Slot-Die Coating
Sheet-based slot-die coating is typically used in research and development settings where individual substrates are coated rather than continuous rolls. This process involves placing a rigid or flexible substrate on a stationary platform, where the coating is applied in a controlled manner.
This method is ideal for:
Prototyping and small-scale research, where precise control over individual samples is needed
Producing high-precision coatings on rigid substrates like glass or silicon
Applications requiring a controlled environment, such as OLED and semiconductor research
Sheet-based slot-die coating provides an excellent way to fine-tune process parameters before scaling up production. Researchers can experiment with different coating viscosities, flow rates, and drying conditions without the constraints of continuous processing.
Roll-to-Roll Slot-Die Coating
Roll-to-roll (R2R) slot-die coating is designed for continuous manufacturing. A flexible substrate is fed through a system of rollers while the slot-die head applies the coating. This method is widely used for large-scale production where efficiency and throughput are crucial.
Roll-to-roll slot-die coating is ideal for:
Scaling up production while maintaining uniform coating thickness
Continuous coating of flexible substrates such as PET, PEN, or metal foils
Industries like solar energy, printed electronics, and batteries, where high-speed manufacturing is necessary
By using R2R slot-die coating, manufacturers can optimize material usage and significantly reduce production costs. The ability to process large volumes efficiently makes it a preferred choice for companies transitioning from research to full-scale manufacturing.
What are the advantages of a roll-to-roll slot-die coater? Explore our in-depth guide to learn more.
Compact vs. Large Slot-Die Coaters
Slot-die coaters come in a range of sizes, each suited to different applications and production needs. The choice between a compact system and a large industrial system depends on factors such as production volume, available workspace, budget, and the level of process automation required.
Compact Slot-Die Coaters
Compact slot-die coating systems are primarily used in research labs, pilot studies, and low-volume production environments. Their small footprint makes them ideal for laboratories where space is limited, and their modular design allows for easy integration with other testing and characterization tools.
One of the main advantages of compact systems is their efficiency in material usage. Since they require less coating solution to operate, researchers can perform high-precision experiments without excessive material waste. This is particularly beneficial for expensive or rare materials, such as advanced battery electrolytes, high-performance polymers, or next-generation photovoltaics.
Compact coaters also provide greater flexibility for researchers experimenting with different coatings. Their modular nature allows for quick adjustments in coating parameters, including slot-die head configurations, drying and curing techniques, and substrate handling. This adaptability makes them valuable for early-stage development, where rapid iteration is key to optimizing formulations and process conditions.
Large Industrial Slot-Die Coaters
At the other end of the spectrum, industrial-scale slot-die coaters are built for high-volume manufacturing and are often integrated into fully automated production lines. These systems accommodate wider substrates, enabling the continuous processing of large-area coatings for applications such as flexible electronics, fuel cells, and roll-to-roll printed solar cells.
Industrial slot-die coaters are designed for high processing speeds, ensuring that manufacturers can scale up from laboratory research to full-scale production without compromising coating uniformity or quality. The ability to coat large substrates with consistent thickness control is crucial for industries that require precise layer deposition, such as the display, energy storage, and medical device sectors.
While large-scale systems require higher initial investment and infrastructure, they offer significant advantages in terms of throughput, repeatability, and long-term cost efficiency. These systems are also more likely to include advanced automation features, such as real-time process monitoring, in-line quality control, and closed-loop feedback mechanisms that ensure optimal coating performance.
Choosing the Right System
For researchers and companies developing new coatings, compact slot-die coaters provide the control and precision needed for small-scale experimentation. Once a process is optimized, industrial slot-die coaters enable the transition to large-scale production, maintaining scalability while ensuring quality and repeatability.
Many manufacturers start with a compact system for early-stage development and then scale up to an industrial system once the coating process is fully optimized. This stepwise approach minimizes risk and allows for a smooth transition from R&D to commercialization.
The LR2RC500 Bundle is probably the world’s smallest R2R Slot-die Coater.
Slot-Die Heads: Materials, Sizes, and Configurations
The slot-die head is the core component of a slot-die coater, playing a crucial role in coating uniformity, thickness precision, and overall process control. Its material, design, and width determine its suitability for various applications, from research-scale experiments to full-scale industrial production.
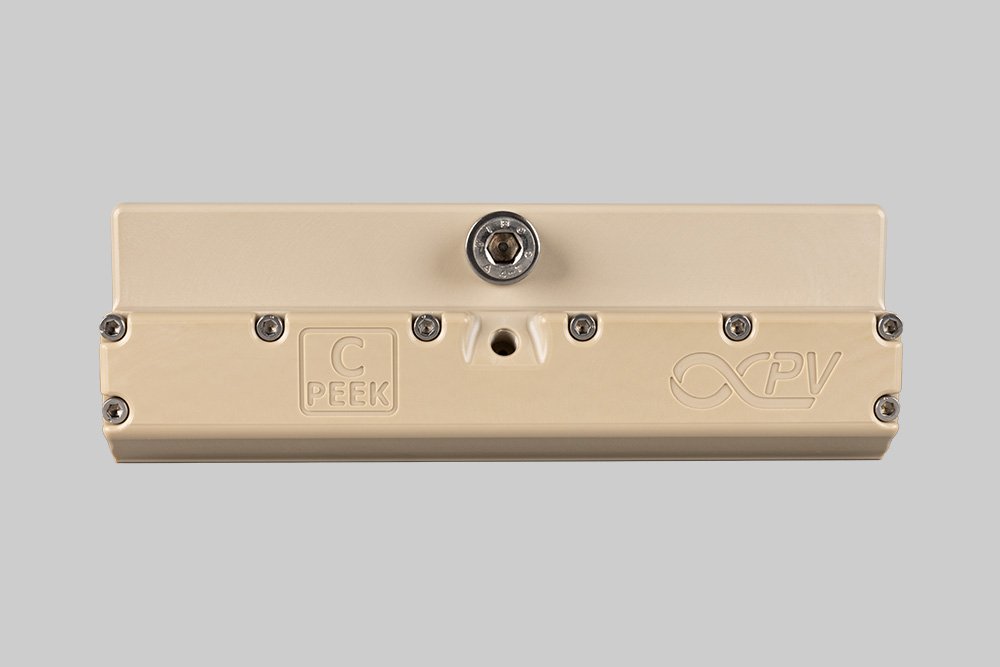
Slot-die heads are typically made from PEEK, stainless steel (316/316L), or titanium. Each material offers distinct advantages.
PEEK is lightweight and highly resistant to chemical corrosion, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring minimal contamination, such as biomedical coatings.
Stainless steel is the most widely used option due to its durability and versatility across different coating processes.
Titanium, on the other hand, provides superior strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for aggressive solvents and high-temperature environments.
The size of a slot-die head is equally important. Small-scale heads (40 mm–120 mm) are commonly used for laboratory research, allowing for precise experimentation with thin-film coatings. Mid-sized heads (150 mm–250 mm) are often seen in pilot production setups, bridging the gap between R&D and industrial manufacturing. Large-scale heads (305 mm and beyond) are used for high-throughput roll-to-roll (R2R) production, where uniformity over wide coating areas is essential.
For certain applications, a heated slot-die head is necessary. Heating helps control fluid viscosity, ensuring a stable coating process and preventing defects like uneven drying or inconsistent layer thickness. This is particularly beneficial for battery electrode coatings, printed electronics, and photovoltaic films, where precise material deposition is critical to performance.
By selecting the right slot-die head material, size, and optional heating functionality, researchers and manufacturers can optimize their coating process for maximum efficiency and quality.
Stainless steel slot-die head.
PEEK slot-die head.
Final Thoughts
A slot-die coater is a precision coating system used to apply uniform thin films to a variety of substrates. Known for its high accuracy, material efficiency, and versatility, this coating technique is essential for applications ranging from energy storage and printed electronics to biomedical devices and functional films. Slot-die coating excels in producing consistent layers, with the ability to scale from small-scale research to large-scale industrial production.
Whether used in a compact research lab setup or a large manufacturing line, slot-die coaters enable controlled deposition of coatings with minimal waste, making them a valuable tool for both experimental development and mass production. With customizable configurations, slot-die coaters can be tailored to specific application needs, ensuring reliable performance in a wide range of industries.
For researchers looking to explore slot-die coating, compact systems like infinityPV’s Slot-Die Coater and Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater provide tailored solutions without unnecessary complexity.
The Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater is fully modular, allowing you to select the precise components needed for your application. Build your own today.
Learn More About Slot-Die Coating
Gong, X., Han, J., Yan, F. et al. Numerical and experimental investigation on formation of the film for different die lip configurations in lithium-ion battery electrode slot-die coating. J Coat Technol Res 21, 481–492 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-023-00874-4
Creel, E.B, Tjiptowidjojo, K., Lee, J.A., Livingston, K.M., Schunk, P.R., Bell, N.S., Serov, A., & Wood III, D.L. Slot-die-coating operability windows for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell cathode catalyst layers. J. Colloid Interface Sci 610, 474-485 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.047
Ding, X., Liu, J. & Harris, T.A.L. A review of the operating limits in slot die coating processes. AIChE J 62, 2508-2524 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15268
Krebs, F.C. Polymer solar cell modules prepared using roll-to-roll methods: Knife-over-edge coating, slot-die coating and screen printing. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 93, 465-475 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2008.12.012.
Related Articles
Get Professional Support for Your Coating Needs
Need help with slot-die coating, coating machines, or any related applications?
Contact infinityPV’s experts today for professional guidance and support.
Related Articles
Slot-Die Coating: 5 Must-Know Tips for Coating Precision and Efficiency
Master slot-die coating with these 5 helpful tips. Avoid common pitfalls, improve coating precision, and ensure smooth, consistent results.
Related Products
Laboratory Roll-to-Roll Coater
A compact and modular high precision roll-to-roll slot-die coater that transforms the way thin functional films are printed and coated.
LR2RC500 Bundle
Probably the world’s most compact R2R slot-die coater. A compact, fully integrated R2R coater that fits on a workbench, in a fume hood or a glovebox.